
Station Name: SHEFFIELD VICTORIA
|
| Date opened: | 15.9.1851 |
| Location: | At the end of Victoria Station Road parallel with Furnival Road |
| Company on opening: | Manchester, Sheffield & Lincolnshire Railway |
| Date closed to passengers: | 5.1.1970 |
| Date closed completely: | 5.1.1970 |
| Company on closing: | British Rail (Eastern Region) |
| Present state: | Demolished - the track through the north part of the site is still in use serving the Stocksbridge Steelworks to the north west of Sheffield. |
| County: | Yorkshire |
| OS Grid Ref: | SK362880 |
| Date of visit: | June 2004 |
Notes: Engineered by Joseph Locke, the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway linking Manchester and Sheffield opened in 1845. Originally, this line terminated at the Bridgehouses station about 1 km to the west of the future Victoria station. In 1847, the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway merged with two other railway companies to form the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway. The station at Bridgehouses had been outgrown and an extension and new station were planned. John Fowler, who later gained fame for co-designing the Forth Railway Bridge in Scotland, was employed to engineer the extension and station. Fowler's design included a 40-foot high, 750-yard viaduct over the Wicker. The extension was completed in 1847–1848 and the new Victoria station opened on 15 September 1851.
The station received a new frontage in 1908 and took on great importance when the line through the Pennines, known as the 'Woodhead Route' after the long Woodhead Tunnel on it which was electrified for freight purposes after World War II.
The electrification of the line reached Sheffield Victoria by 1954, reducing the journey time to Manchester to 56 minutes. This was the first main line in the UK to be electrified, but the only one at 1500 V d.c., a system which was already obsolescent. From this point onwards, all passenger trains heading to Manchester required a change of locomotive at Victoria to a British Rail Class 76 or express passenger British Rail Class 77. Although the 1950's saw services at the station reach their peak, this period also marked the beginning of its decline. As road traffic grew and the mills closed, the surviving coal trains became shorter and more sporadic in operation. In 1953 Barnsley was an early casualty as the line ran almost parallel to the former Midland Railway's Sheffield Midland - Barnsley line, serving mostly the same communities. By the end of the decade, the expresses to Marylebone were either cut or re-routed to Kings Cross (in the case of The Master Cutler). In the mid-1960's there was a concerted effort to concentrate Victoria's remaining local and express train services at Sheffield Midland, leaving Victoria with just an hourly Manchester service and the daily Liverpool-Harwich 'Continental'.
The station re-opened very briefly in 1972 for diverted trains while Sheffield Midland was closed for re-signalling.
See the Lincolnshire & East Yorkshire Transport Review for additional pictures of Sheffield Victoria Station in the 1980's. BRIEF HISTORY OF THE GREAT CENTRAL RAILWAY BETWEEN SHEFFIELD AND LONDON
In order to fulfil his ambitions, Watkin also became Chairman of the Metropolitan Railway who were in the process of extending their line northwards towards Rickmansworth and the South Eastern Railway connecting London with Dover. Initially, Watkin tried to convince other companies to build links with the MS & L allowing him to reach London but he was unable to reach agreement and eventually was left with little option than to build his own line southward from Sheffield to reach the Met. In the 1890's the MS&LR began construction of its 'Derbyshire Lines', in effect the first part of its push southwards. Leaving its east - west main line at Beighton Junction, some 5 1/2 miles east of Sheffield, the line headed south through the Nottingham coal field with a branch line serving its new Central Station in Chesterfield. In July 1890 the MS&LR obtained another act to extend from Chesterfield to Heath creating a loop line. Work started on this new section, of some 4¾ miles, before construction on the original line was finished and opened in July 1893. In 1893 the MS&LR obtained Parliamentary approval to extend this line to London (known as the ‘London Extension’. Construction of the 92 mile route started in 1895 and on 1st August 1897 the company changed its name to the Great Central Railway; it was the last 'main line' to be built until the Channel Tunnel rail link in 2003.
The new line was built from Annesley in Nottinghamshire to join the existing Metropolitan Railway which had now reached Quainton Road in Buckinghamshire, where the line became joint Met/GCR owned (after 1903), it returned to GCR metals near Finchley Road for the final section into Marylebone.
In the 1923 grouping, the Great Central became part of the London & North Eastern Railway which brought an increase in freight traffic from the south Midlands and south west England but the LNER's main north - south route was into London Kings Cross so the Great Central was always considered as a secondary route. After nationalisation, the line became part of British Railways Eastern Region but was transferred to the London Midland Region in 1958. By this time the service was already in decline with the increasing popularity of the car and it was unable to compete with other north - south routes as the line passed through sparsely populated areas south of Rugby. Manchester to London express services were withdrawn on 2nd January 1960 leaving only three semi-fast trains a day and it came as little surprise when the line became the first main line to close in the Beeching era. Beeching considered that the Great Central was a duplicate route which could be sacrificed in favour of the Midland main line.
The shuttle service between Nottingham and Rugby lasted until 3rd May 1969. As closure approached a group of railway enthusiasts got together to discuss the possibility of buying a section of the track to operate preserved steam locomotives. A steam service was reinstated between Loughborough and Quorn in 1973 and in 1976 Charnwood Borough Council agreed to purchase the land from BR and lease it to the railway for 99 years. Despite a shaky start, the Great Central Railway PLC are now operating throughout the year between their headquarters at Loughborough Central and a new station called Leicester North just inside the city boundary. The remaining track between Leicester - Rugby was lifted in early 1970.
The NTHC's aim was to reinstate the remaining line into Loughborough where it joins the GCR
With our motorway network now working at capacity there have been a number of proposals to reopen other sections of the Great Central main line and in 2006 Central Railway was formed to look into the feasibility of building a new rail link from central England to the Channel Tunnel which would include rebuilding part of the Great Central route south of Rugby reviving a 1990’s government proposal to reopen that section of the line as part of a fast rail link from Scotland to the Channel Tunnel. Preservation group web sites: The Buckinghamshire Railway Centre, The Great Central Railway (steam service between Loughborough and Leicester North) & Nottingham Transport Heritage Centre (steam service between Ruddington and Loughborough)  Selected other web sites: The Transport Archive contains further detailed history of the Great Central plus a vast collection of 2344 'on line' photographs many ( the Newton Collection) taken during the construction of the London Extension. Chris Ward's Annesley Web site featuring numerous photographs of the Great Central around Nottingham and the Annesley Motive Power Depot. Great Central Railway through Leicester. Nigel Tout's web site with numerous photographs of the Great Central remains around Leicester and a series of archive photographs of the line. Bridging the Gap details ongoing work to reinstate the link between the two preserved lines. The Great Central Railway Society promotes an historical interest in the Great Central Railway. Selected other web sites: The Transport Archive contains further detailed history of the Great Central plus a vast collection of 2344 'on line' photographs many ( the Newton Collection) taken during the construction of the London Extension. Chris Ward's Annesley Web site featuring numerous photographs of the Great Central around Nottingham and the Annesley Motive Power Depot. Great Central Railway through Leicester. Nigel Tout's web site with numerous photographs of the Great Central remains around Leicester and a series of archive photographs of the line. Bridging the Gap details ongoing work to reinstate the link between the two preserved lines. The Great Central Railway Society promotes an historical interest in the Great Central Railway.
Selected further reading: Great Central Memories by John MC Healey published 1987 by Baton Transport ISBN 0 85936 193 4 - heavily illustrated history of the London Extension. Great Central Then and Now by Mac Hawkins - published (2nd edition) by BCA 1992 ISBN 0 7153 9326 X , station by station photographic survey of the Great Central between Sheffield and London with numerous 'then and now' photographs. See also Sheepbridge & Brimington Station and construction of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway through Brimington by Philip Cousins. Published in St. Michael & All Saints, Brimington parish magazine. (Click here for full text). All tickets from Michael Stewart. Too see other stations on the Great Central Railway between Sheffield Victoria and Aylesbury click on the station name: Aylesbury, Waddesdon, Quainton Road (1st site), Quainton Road (2nd site)**, Calvert, Finmere, Brackley Central, Helmdon, Culworth, Woodford Halse, Charwelton, Braunston & Willoughby, Rugby Central, Lutterworth, Ashby Magna, Whetstone, Leicester Central, Leicester North***, Belgrave & Birstall, Rothley**, Swithland****, Quorn & Woodhouse**, Loughborough Central**, East Leake, Rushcliffe Halt**, Ruddington, Ruddington Factory Halt, Arkwright Street, Nottingham Victoria, Carrington, New Basford, Bulwell Common, Bulwell Hall Halt, Hucknall Central, Annesley South Junction Halt, Hollinwell & Annesley, Kirkby Bentinck, Tibshelf Town, Pilsley, Heath, Staveley Central, Renishaw Central, Killamarsh Central, Beighton (1st site), Woodhouse Junction, Woodhouse*, Darnall*, Sheffield Victoria & Sheffield Bridgehouses. |
victoria_old27.jpg)
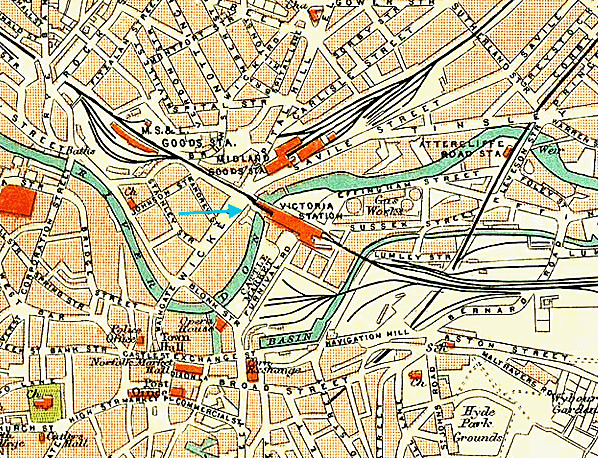
1890's - note the goods station to the north west of the passenger station. The goods station to the north west of Sheffield Victoria is the former Sheffield Bridgehouses passenger terminus.
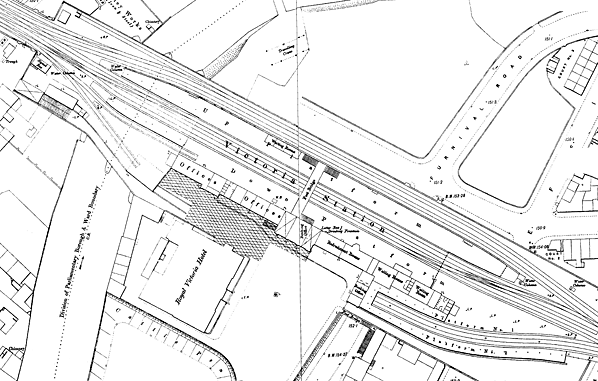 OS 1:500 Town plan showing the layout of the station in 1890. Click here for a larger version.
OS 1:500 Town plan showing the layout of the station in 1890. Click here for a larger version.victoria_old3.jpg)
Copyright photo from John Alsop Collection
old28.jpg)
Photo copyright Colour-Rail
old46.jpg)
Photo by David Faircloth
victoria_old6.jpg)
Photo by Bevan Price
victoria22.jpg)
Sheffield Victoria Station looking west in 1980. The track on the far side of the station remained in use at this time.
Photo by Alan Weaver
victoria34.jpg)
station in March 1981.
Photo by Andy Hoare
victoria2.jpg)
victoria30.jpg) Sheffield Victoria Station looking east in February 1983. This is the Sheffield Midland to Huddersfield service which reverses to the east of the station passing through the closed Sheffield Victoria Station.
Sheffield Victoria Station looking east in February 1983. This is the Sheffield Midland to Huddersfield service which reverses to the east of the station passing through the closed Sheffield Victoria Station.Photo by Alan Weaver
victoria3.jpg)
Photo by Rob Woods from Rob's Railway Image Galleries
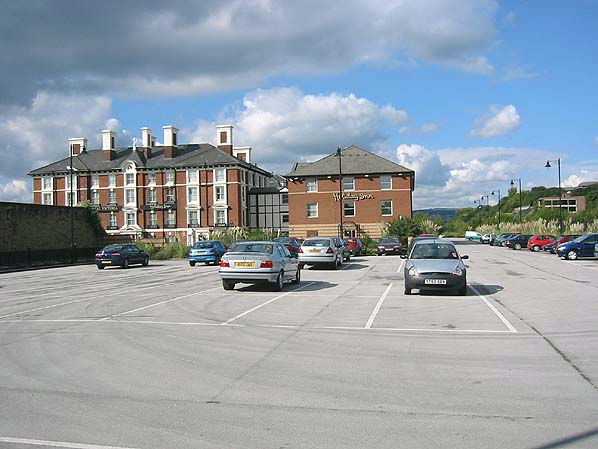

The site of Sheffield Victoria Station in 2004
Photo by Paul Chilver
Click here for more pictures of Sheffield Victoria Station

|
| Last updated: Friday, 26-May-2017 10:55:54 CEST | © 1998-2014 Disused Stations |









 Home Page
Home Page