Note: In some official railway publications the station has been referred to as Newbiggin-by-the-Sea, for example in the Railway Clearing House Handbook and on Lance Cattermole’s BR (NE) poster map of Northumberland published in 1949. The longer version of the name was also used on some tickets.
Newbiggin was a mining village and aspiring coastal resort when the railway arrived in 1872. In 1911 the NER recorded the station’s catchment population as 3,736, and by 1951 Newbiggin was a town of a little over 10,000 people.
1.gif) |
The station building was H-plan with an elongated central section, and constructed largely of brick. Dutch gables with spike finials adorned the two-storey west and single-storey east wings, making this the most attractive station in the Blyth / Newbiggin area. The platform elevation included a slightly projecting ground floor window on the west wing, and a debased |
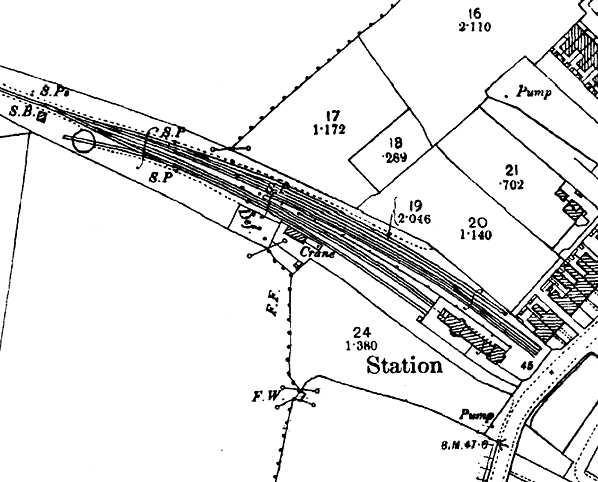
Venetian window on the east wing. These window styles were repeated, with minor variations, on the road frontage. Door openings had restrained gothic arches. An open-fronted verandah -removed by 1962- stretched between the cross wings. The main platform (about 200yd) and bay (about 120yd) received a narrow 43yd extension in 1902 to accommodate longer excursion trains. The signal box was about 100yd west of the station, south of the running lines and adjacent to a siding which served a turntable. The goods facilities included a one-ton crane; a range of goods could be handled but (in 1913) potatoes and livestock were the principal traffic.
Documents held in the National Archive, Kew, reveal that in 1924 the LNER planned additional capacity. Scheme 1 would double the line to Woodhorn (one mile west of Newbiggin) and create a new station with two curving 130yd platforms on sidings north-west of the original station. The main building, reached by a new approach road, would be on the up platform, with a waiting shed on the other platform. Scheme 2 was to add a 200yd platform opposite, but displaced westwards from, the existing main platform. Neither scheme was adopted. After closure in 1964 the tracks were removed between Newbiggin and Woodhorn, and the station site was cleared by the mid-1970s.
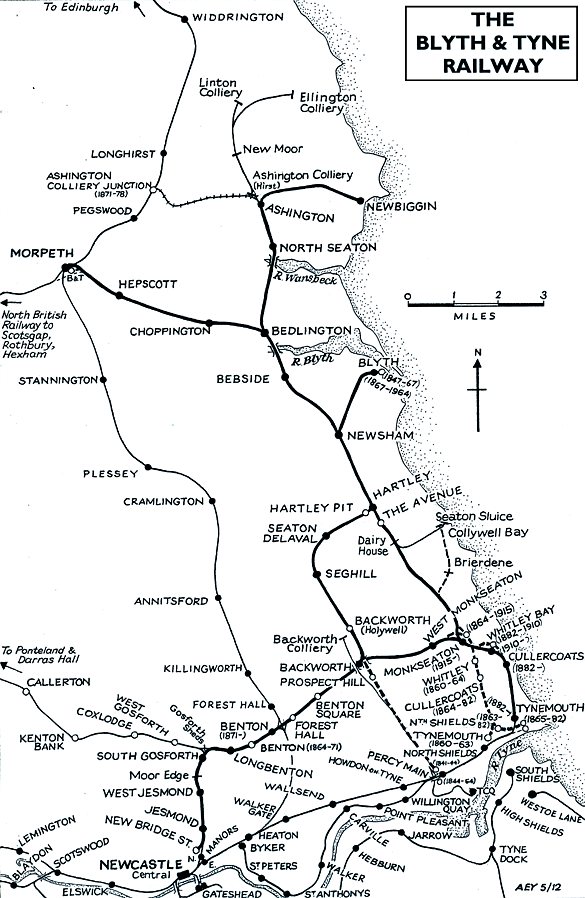
BRIEF HISTORY OF BLYTH & TYNE RAILWAY (Percy Main to Blyth, Morpeth & Newbiggin)
Development of the B&T
The system’s development is inseparable from the growth of coal mining. From the 16th century coal was mined in shallow pits close to the River Tyne. By the early 17th Century, there were pits further north. In 1605 Huntingdon Beaumont, a Nottinghamshire businessman, obtained permission to extract coal in Bedlingtonshire (then a detached part of County Durham). Beaumont had installed a wooden waggonway - possibly the world’s first - at Wollaton (Nottinghamshire) to carry coal to the River Trent.He applied this technology to his Northumbrian operations, and by 1608 waggonways conveyed coal from his pits at Bedlington, Bebside, and Cowpen to the River Blyth. It was shipped to London, where coal from the ‘Great Northern Coalfield’ was in demand. Beaumont’s pits proved unprofitable, and his financial embarrassment caused the closure of his waggonways in 1618.
| It is probable that about a century passed before other waggonways opened in south-east Northumberland. By the mid nineteenth century there were at least a dozen of them in the Blyth & Tyne area. The most significant in B&T history was the Seghill Coal Company’s waggonway. This firm used the Cramlington Waggonway but grew dissatisfied with the |
 |
facility. Seghill’s own line to the River Tyne at Percy Main opened for coal traffic on 1 June 1840. From 28 August 1841 passengers were conveyed in trains which were certainly rope-hauled south of Holywell. The winding engine was situated at Prospect Hill. Stations were at Seghill, Holywell, Prospect Hill, and Percy Main. In June 1844 the Newcastle & North Shields Railway began to work the Seghill passenger and goods trains. By December 1847, what had become the Blyth, Seghill & Percy Main Railway was calling itself the Blyth & Tyne. In 1853 the company began the work to cut through Prospect Hill and reduce the gradient up from Percy Main so that locomotives could replace rope haulage. The 1:55 climb, prior to easing of the gradient, was too steep for locomotives of the day to tackle.
The Seghill railway was extended on 3 May 1847 when passenger trains reached Blyth, serving Seaton Delaval Colliery and Hartley Pit on the way. This line was primarily to carry coal from pits near Blyth to the Tyne for export, since the River Blyth was relatively shallow. The May 1849 timetable showed three weekday departures from Blyth for the hour-long journey to Percy Main, three return workings, and an extra Percy Main-Seaton Delaval train.
From 1851-3 passengers could change at Hartley Pit onto a train that intermittently operated on a waggonway to Seaton Sluice via Dairy House. The service ceased when the B&T restricted passenger trains to their ‘main’ line. Seaton Sluice never again had passenger trains. The ‘Collywell Bay’ branch reached the village from Monkseaton in 1914, but it was not opened and was dismantled in 1931.
 |
From Newsham, the Bedlington Coal Company opened a 2¾-mile branch to Bedlington for coal traffic on 12 June 1850. The B&T provided passenger trains from August 1850. In 1851 the service was three trains each way on weekdays, and two on Sunday - the same frequency as on the Blyth-Percy Main route. Passenger stations were at Newsham, Cowpen Lane |
(renamed Bebside in April 1860), and Bedlington. The B&T bought the line in 1855. A wooden viaduct 257yd long and about 80ft high crossed the River Blyth. In 1929 it was replaced with a steel structure, on a slight deviation.
Incorporated on 1 January 1853, the B&T braced itself to repel companies that might intrude on its patch.
In August 1853 Royal Assent was obtained for its Newsham-Bedlington line (where it already operated passenger trains for the Bedlington Coal Company: the B&T bought the line in 1855) and on to Morpeth.
This Assent also allowed upgrading of the Hartley-Dairy House waggonway. In July 1854 Parliament approved B&T plans to extend the latter route to Tynemouth and construct northwards to Longhirst on the East Coast main line. Passenger and goods trains were introduced between Bedlington and Morpeth on 1 April 1858. The track was single from Choppington to Morpeth (except through Hepscott). Until May 1880 Bedlington trains used the B&T’s Morpeth station.
The B&T reconsidered plans for northward extension, and in August 1857 Royal Assent was obtained for a Bedlington-Warkworth Harbour line via Bothal Demesne, Woodhorn, Linton, and Warkworth; the Longhirst scheme was dropped. The outcome was a two-mile branch to North Seaton which opened to all traffic in November 1859. No further progress was made at this stage, but Assent was obtained in June 1861 for a branch line to Newbiggin, upon which they did not act. In August 1867 a further Bill to construct to Warkworth Harbour, with a branch to Newbiggin, was successful.
.gif) |
On 1 March 1872 the line beyond North Seaton opened, consisting of the first mile of the Warkworth Harbour line, and the 2¼-mile Newbiggin branch, which swung sharply east from the intended ‘main line’. A massive wooden viaduct crossed the River Wansbeck; 400yd in length and 85ft above water level, it was reputedly the largest wooden structure in Britain; a steel structure replaced it in 1929.
With the exception of Blyth (1894-6), Morpeth and Newbiggin the stations on the B&T, north of the ‘Coast Circle’ were generally modest and utilitarian affairs, reflecting the dominance of the third-class, local traffic. Brick was the preferred material of construction, except at Morpeth, Hepscott and Choppington where sandstone was used. At Newsham, although the platform buildings were of brick, the stationmaster’s house was stone-built
An intermediate station appeared in the NER timetable from May 1878 at Hirst, later renamed Ashington. The Warkworth Harbour line was never built, so Newbiggin remained the northerly passenger terminus. However a network of mineral lines, some owned by Colliery companies over which the B&T/NER/BR had running powers, eventually extended north to Ashington, Linton, Ellington, Lynemouth, Newbiggin, and Woodhorn collieries, and opencast mines at Longhirst (and more recently, Butterwell). The Alcan aluminium smelter, built in 1968, was also served. One further addition to the ex-B&T system was mooted in 1894, when the NER sought to build a Blyth-Cramlington line. Opposition by Lord Hastings, who feared losing revenue from ‘wayleaves’ on existing routes through his land, caused the Bill to be dropped.
B&T motive power and freight traffic
Locomotives on the B&T before absorption by the NER were generally 2-4-0 tenders for passenger and goods, and 0-6-0 for coal trains. Various builders were used, including Robert Stephenson and Timothy Hackworth. Some engines were constructed by the B&T at Percy Main. In NER days, from 1874, freight was hauled by classes 8, 44, 59, 124, 290, and 398. From 1886 C class 0-6-0 and P class joined the others. On the coal staiths, shunting duties were left to 0-6-0 tanks, and later diesel classes 03 and 08. K1 and 4MT 2-6-0 locomotives hauled freight after Nationalisation, followed by diesel classes 17, 20, 37, and more recently class 56.
| Shortly before World War I, G5 0-4-4Ts, operating ‘Push and Pull’ ‘autocars’, took over many passenger duties. Passenger stock in NER/LNER days comprised a mixture of clerestory coaches (built 1896-1906), low-roofed stock (built 1899-1906) and later elliptical roofed coaches, all of NER origin. From 1927 the LNER introduced single-unit Sentinel Cammell and |
4.gif) |
Clayton steam railcars in NE England. They operated on the former B&T lines; the Sentinel Phenomena spent its working life plying mainly between Blyth, Morpeth, and Monkseaton. From 1937 G5 ‘Push and Pull’ operations were re-introduced, and steam railcars were abandoned by 1948. Passenger services to Blyth and Newbiggin were dieselised in September 1958. However the 5:30 am parcels train ex-Newcastle, returning as the 7:35 am ex-Newbiggin remained steam-hauled.
Locomotives were stabled at Percy Main (formerly the company’s workshop) until 1966; South Blyth (1879-1968); and North Blyth (opened 1897-1968). A diesel depot opened at Cambois in 1968.
Although passenger services operated successfully for many years, goods and mineral traffic created the B&T and has sustained much of the system since 1964, when passenger trains ceased. Coal export via staiths at Blyth and (from 1867) Cambois was vital to the railway. To convey coal to the ports, the network steadily improved in the late nineteenth century. Cambois was rail- connected from 1867. Pits west of Ashington were linked directly to the ex-B&T at Ashington in 1886, saving coal trains the circuitous journey via Pegswood, Morpeth (reverse), and Newsham (reverse again) to Blyth. The congested Newsham-Blyth staiths branch was supplemented by another line in 1888, the year when further staiths were built at Blyth. In the 1890s rail facilities at Cambois were enlarged, and staiths were built at North Blyth. In 1896 a curve from Marchey’s House Junction to Winning Junction opened off the Bedlington-Ashington line enabling Ashington coal to reach North Blyth / Cambois directly.
In the early twentieth century some fifty collieries operated in the ex-B&T area. Port facilities continued expanding, further staiths opening at Blyth in 1928. Blyth handled other freight too, including timber and fish. The port reached its zenith in the early-1960s when almost 6.9 million tonnes of coal were exported, making Blyth Europe’s leading coal shipping port. However, from the mid-1960s Northumberland’s collieries closed, Ellington being the last survivor until it closed in 2005. The decline was partly offset by the opening of opencast mines, notably Butterwell (near Ashington) which prospered in the 1980s-90s.
 |
The coal-fired power station at Cambois (in operation from 1958 until 2001) used the railway, and the aluminium smelter at Lynemouth (opened 1968) continues to be served by rail, with double-track access However production of aluminium ceased in March 2012 and the factory closed in May 2012.. Throughout the 1950s road lorries coaxed freight away |
from Britain’s railways. The ex-B&T system was no exception, with goods handling ceasing at all stations in 1963-65. Bedlington handled parcels traffic until 1966. By 1990 only coal, alumina, and aluminium were carried. West Blyth staiths closed in 1989, and a new facility opened at Bates in 1991. In 1980 a new curve between Hepscott North and Morpeth North junctions allowed direct access to and from Scotland. Former double-track sections were singled: Bedlington-Choppington (1973) and Newsham-Backworth (1985). Since 1980 anew single-track has allowed independent working from Backworth to Benton Quarry on the ECML, avoiding conflict with Metro services.
B&T passenger services
The B&T system’s layout allowed many permutations of passenger train services, and these changed over the years. Bradshaw of April 1910 showed an exceedingly complex set of train workings.
| By 1920 frequencies were generally reduced, except on the Manors North-Morpeth service. An intensive bus network developed in the 1920s between the closely spaced towns, and train loadings declined. Bedlington-Morpeth trains were particularly vulnerable to competition because the towns’ stations were away from their centres. By summer 1946 only two trains used the route, both towards Morpeth: from Blyth (dep. 6:45 am) and Bedlington (dep. 8:45 a.m.). In summer 1948 only the 6:45 am ex-Blyth was running. A British Railways’ review of the Bedlington-Morpeth service noted that only 1,554 local and 76 other passengers were carried in 1948, receipts totalling £61. Parcels traffic was worth £198, but freight originating from the line earned £80,695. The review recognised that ‘regular passenger traffic is negligible; the two branch stations are principally used on the annual Northumberland Miners’ Gala day at Morpeth and for occasional excursions’. BR proposed closure to passengers, with occasional reopenings for Gala and excursion trains. Loss of passenger revenue was |
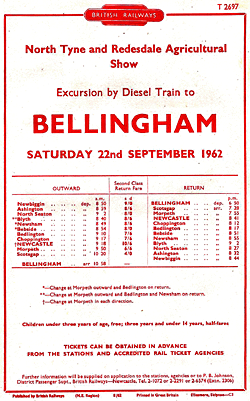 |
estimated at £22, but income could be derived from letting the general and ladies’ rooms at Choppington and Hepscott. Bedlington UDC’s suggestion that reduced fares would attract custom found no favour with BR who withdrew the passenger train 1950. In the final months the two regular passengers were lavishly provided with three or four suburban coaches. How things had changed from 1911 when the intermediate station at Choppington issued almost 116,000 tickets. By summer 1950 the B&T timetable was threadbare between weekday morning and evening peak hours; Monkseaton-Blyth, for instance, had no service between the 9:12 am ex-Monkseaton and 4:40 pm ex-Blyth. Saturday trains were more numerous, as in previous years, catering for shopping and leisure journeys. From January 1955 the services were focussed on Monkseaton, to reduce operating costs and improve connections to north Tyneside suburban coastal stations. After diesel multiple units were introduced in June 1958, a regular interval hourly Saturday service was introduced of trains between Monkseaton and Blyth connecting at Newsham with Manors – Newbiggin trains, which themselves connected with Newsham – Blyth trains. The revised B&T weekday and Saturday services differed enough to require separate listings in the NE Region timetable. Sunday trains were withdrawn by summer 1954.
6.gif) |
Beeching earmarked the ex-B&T for closure, the proposal being published on 8 November 1963. On 30 July 1964, despite objections, the Minister of Transport consented to the withdrawal of passenger services. Ashington, with a population of almost 30,000, and Blyth with about 40,000 would become two of the largest British towns to lose their trains, but |
the ‘closure culture’ was strong –not least among BR senior officials. The enhanced Saturday service, introduced in 1958, had not produced the substantial increase in passenger use that had been hoped for, and in the early 1960s there seemed to be no inclination to make further improvements or effect economies by de-staffing stations. The concept of ‘park-and-ride’ stations was in its infancy at that time, with consideration being given to providing such a facility at Forest Hall, on the East Coast main line and at New Pudsey in Yorkshire – the latter was opened in 1967. However there is no evidence that such stations were ever proposed for the Newbiggin / Blyth lines.
The final train left Blyth at 11:59 pm for Newbiggin on Saturday 30 October, and official closure followed two days later. Freight services continued except for Monkseaton-Hartley, Woodhorn-Newbiggin, and Blyth Signal Box-Blyth station, which closed entirely. After passenger closure, excursions continued from Newsham. In 1968 the Isabella-Blyth Shed branch closed.
Since closure to regular passenger services East Coast main line passenger trains have occasionally been diverted over the system: the Morpeth NE curve made this operation much simpler. However withdrawal of ECML overnight passenger services (1988), route electrification (1991), and bi-directional ECML signalling have reduced diversions.
At the southern end of the B&T system the North Tyneside Steam Railway has adopted the Seghill Waggonway trackbed. The Stephenson Museum was completed in 1989, and passenger trains commenced in 1991. They now run from Percy Main station (SW of the Metro station) northwards via the museum to the Rising Sun underbridge.
| Almost fifty years after their withdrawal, it is hoped that passenger services on the Backworth-Newsham-Ashington section will be restored as a response to increased road congestion and long road journey times, especially in the rush hours. South East Northumberland Rail Users Group (SENRUG) is convinced that there is strong local support for |
7.gif) |
reopening. (See their website) Their first priority is to reinstate the B&T section that lost its passenger services first, from Morpeth to Bedlington: this should need minimal investment in infrastructure - new platforms at Choppington and Bedlington - and a simple extension to an existing local service from Newcastle Central to Morpeth that is stabled in the B&T sidings at Morpeth for the time it would take to run to Bedlington and back.
Stations
Because stations opened at different times, and some were relocated or rebuilt, they varied in design. They were generally of limited architectural quality. Several were designed by J F Tone, who was engineer of the line from 1855. Tone was also engineer of the Border Counties and Wansbeck Valley Railway, but there is no obvious similarity between the station designs on these lines and those on the B&T. Compared with most Northumbrian stations they were well patronised as seen below. However comparison of 1911 and 1951 ticket issues shows the huge impact of bus competition. In 1951 Seghill, North Seaton, Ashington and Newbiggin had only 14% of the 1911 traffic; only Hartley (96%) retained its traffic.
| |
Tickets issued 1911 |
Tickets issued 1951 |
Regular passengers
TUCC Report 1964 |
Seghill |
39,020 |
5,499 |
23 |
| Seaton Delaval |
77,375 |
17,376 |
0 |
| Hartley |
46,999 |
45,135 |
100 |
| Newsham |
133,659 |
61,499 |
174 |
| Blyth |
348,623 |
62,594 |
74 |
| Bebside |
57,324 |
9,109 |
22 |
| Bedlington |
227,121 |
52,791 |
100-120 |
| North Seaton |
100,192 |
13,845 |
3 |
| Ashington |
257,883 |
39,778 |
54 |
| Newbiggin |
165,927 |
23,514 |
182 |
| Choppington |
115,642 |
closed |
closed |
| Hepscott |
13,961 |
closed |
closed |
Latterly all stations were gas lit, except Hepscott with oil lanterns, and North Seaton, Choppington and Ashington with LNER electric lighting on swan-neck posts. LNER wooden nameboards with raised metal letters were standard; BR totems signs were not installed.
Click here for a list of sources and a Blyth & Tyne bibliography
Tickets from Michael Stewart except 1140 & 4859 C J Dean and 0000, 1494 Brian Johnson. 1950 Bradshaw from Nick Catford, 1962 timetable from Chris Totty. Route map
drawn by Alan Young.
To see other stations on the Blyth & Tyne Railway Percy Main - Blyth, Morpeth & Newbiggin line click on the station name: Percy Main (B & T) 1st site, Percy Main (B & T) 2nd site, Prospect Hill, Backworth (1st site), Seghill,
Seaton Deleval, Hartley Pit, Hartley, Newsham, Blyth 2nd site, Blyth 1st site (on branch), Bebside, Bedlington, Choppington, Hepscott & Morpeth B & T.
Newbiggin line: North Seaton & Ashington |

old12.jpg)
old2.jpg)
old6.jpg)
old1.jpg)
old14.jpg)
old1.jpg)
old4.jpg)
old5.jpg)
old10.jpg)
4.jpg)

1.gif)


.gif)
4.gif)

.gif)

6.gif)
7.gif)
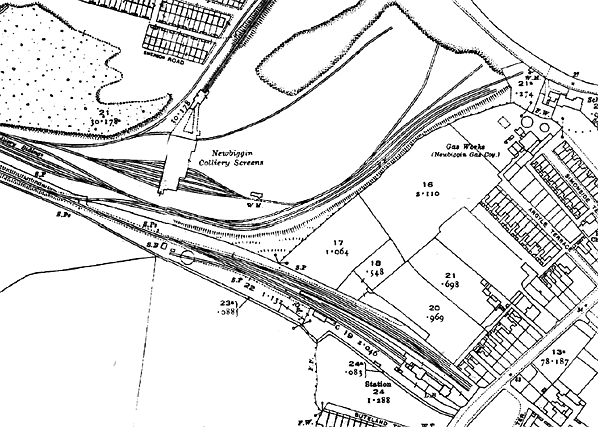
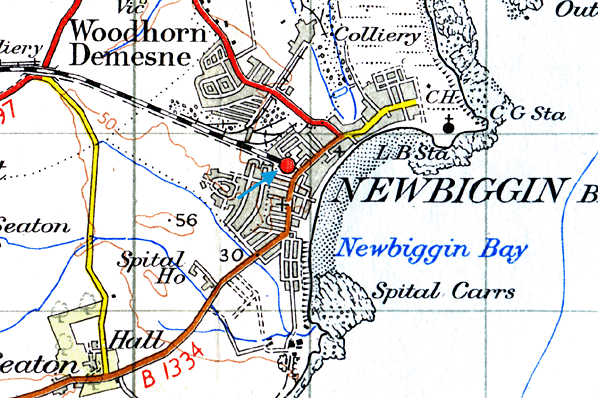
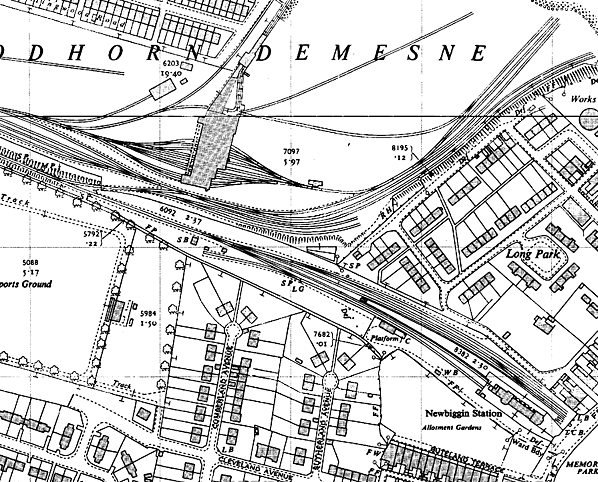 1958 1:2500 OS Map. There are still many sidings in the vicinity of Newbiggin station testifying to the importance of mineral traffic on the branch. Urban development encloses the station site.
1958 1:2500 OS Map. There are still many sidings in the vicinity of Newbiggin station testifying to the importance of mineral traffic on the branch. Urban development encloses the station site.old7.jpg)
old9.jpg)
old_thumb3.jpg)
old_thumb8.jpg)
old_thumb13.jpg)
old_thumb15.jpg)
old_thumb11.jpg)


 Home Page
Home Page