
Station Name: LLANDYSSUL
|
| Date opened: | 3.6.1864 |
| Location: | East side of Station Road |
| Company on opening: | Great Western Railway |
| Date closed to passengers: | 15.9.1952 |
| Date closed completely: | 6.9.1965 |
| Company on closing: | British Railways (Western Region) |
| Present state: | The station site is lost under the Llandyssul bypass. A grain warehouse and a saw-mill are still standing in the goods yard (10.2012) but the yard has been sold for redevelopment. The stationmaster's house, which overlooks the station site, is in private occupation |
| County: | Cardiganshire |
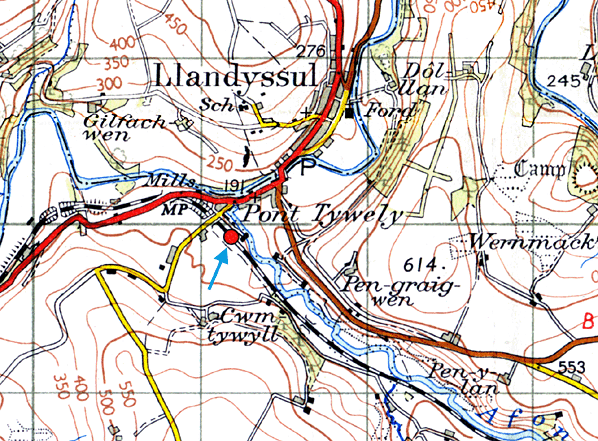
| OS Grid Ref: | SN411400 |
| Date of visit: | 11.9.2012 |
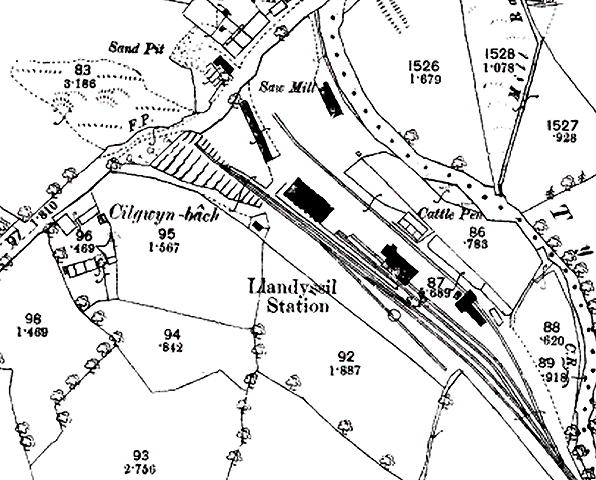
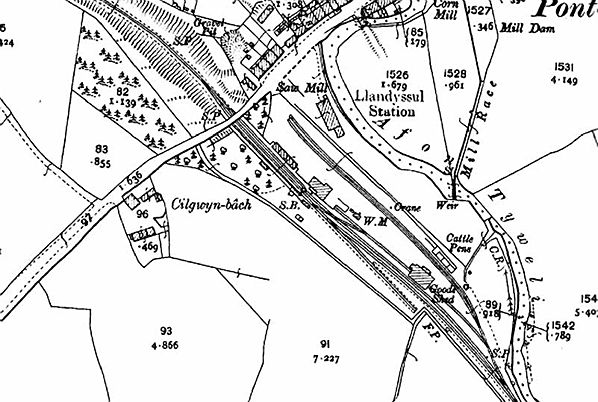
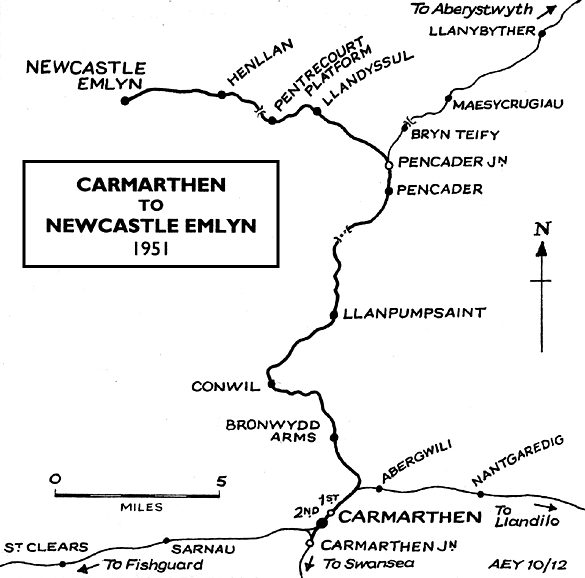
Notes: Llandyssul was one of the larger communities on the Newcastle Emlyn line, with a population of 2902 in 2001. The Teifi Valley around Llandyssul was the home of the Welsh woollen industry. Many sheep were reared locally, and there were plenty of fast-flowing streams to power machinery, so many woollen mills were established in the area in the nineteenth century. There was also a flannel shirt factory in the village at that time. Almost all of the mills had closed by the end of the twentieth century as cheaper textiles became available from the far east. The spelling of the village name has changed over the years. Early Ordnance Survey maps show the village as Llandyssil, but by the early twentieth century it was Llandyssul and in the 1950s it became Llandysul. These changes of spelling were reflected in the station name, and it was only in its final years as a goods station that the final form of spelling was used for the station. (The spelling used for the page title is Llandyssul which was the spelling at the time of closure to passengers) Llandyssil station, which was actually closer to the village of Pont Tywely (Pontwelly), opened on 3 June 1864 when the Carmarthen & Cardigan Railway was extended from its temporary terminus at Pencader. It was intended that Llandyssil should also be a temporary terminus, but it was a further 31 years before the line was extended to Newcastle Emlyn by the Great Western Railway. As built, the station had a single platform on the down up side of the line with a reversing loop opposite the platform. The goods yard was on the up side, largely behind the passenger station; it comprised two sidings terminating either side of a loading dock behind the platform, one of which passed through a large goods shed. A third siding ran along the north side of the yard passing a cattle dock and pens to terminate close to a saw-mill at the entrance to the goods yard. On 3 August 1864 the C&CR opened a one-road engine shed at the station. The shed with an adjacent water tank was built in the goods yard close to the cattle dock, with the northern most siding passing through it. A turntable was also provided on a short siding reached from the passing loop. There was no signal box. The line from Pencader to Carmarthen was converted to mixed gauge from 1 November 1866 to allow trains from Aberystwyth to reach Carmarthen, but the three-mile line from Pencader to Llandyssil remained broad gauge until 1 June 1872.
The station name was changed to Llandyssul on 17 December 1918. A large concrete-panelled grain store with a pitched asbestos roof - standing on staddle stones, to deter rodents - was built at a later date, probably during WW2 The passenger service was withdrawn on 15 September 1952, but the station remained open for goods traffic. There was a further name change to Llandysul in May 1957. Goods services were withdrawn from 6 September 1965, and the passing loop was quickly lifted. The station buildings, with the exception of the down platform waiting room, had been demolished by the end of the decade. The majority of the goods yard buildings remained standing. After closure, a coal merchant continued to operate from the yard, and a fortnightly livestock market was held there until 2008 when construction of the Llandysul market started. The large grain warehouse was a retail outlet for West Wales Rally Spares. The 1.8 acre site, including the remaining buildings, has recently been sold for commercial redevelopment for £145,000. It is assumed that the buildings will be demolished. for £145,000. BRIEF HISTORY OF THE CARMARTHEN & CARDIGAN RAILWAY The Carmarthen & Cardigan Railway Company was formed in 1854 to promote a broad gauge railway from a junction with the SWR at Carmarthen. Initially the line would terminate at Newcastle Emlyn, a distance of 26¾ miles, later to be extended 12 miles to Cardigan where the company intended to build a deep-water port. The Carmarthen & Cardigan Railway was incorporated by an Act of 1 July 1854 to build the line between Carmarthen and Newcastle Emlyn. There was authorised capital of £300,000 with powers to borrow a further £80,000. City of London-based contractor John Jay was employed to build the line. Jay's previous railway contracts included Stoke-on-Trent railway station, and a section of the Great Northern Railway north of King's Cross together with King's Cross goods station and passenger terminus; these were all built around 1850.The line was to be constructed in two stages, with the first 18-mile section linking Carmarthen and LLandyssil. Work started a mile south of Carmarthen following the ‘turning of the first sod’ in March 1857; a junction was made with the South Wales Railway at Myrtle Hill. The main engineering obstacles facing engineer Joseph Cubitt were the construction of a crossing over the River Towy at Carmarthen and the excavation of a tunnel between the valleys of Skanda Vale and Dolgran, under the Brechfa Forest south-west of Pencader. During construction in 1859, the C & CR attempted to switch from broad gauge to standard gauge, which would have meant that all railway infrastructure could be built to smaller (and thus cheaper) dimensions. Such a change would require the approval of Parliament, and pressure was put on the company by the South Wales Railway which did not want the rival standard gauge making an incursion on its territory; a Bill authorising this change of gauge was never put before Parliament. The first mile to a terminus at Carmarthen opened on 1 March 1860 after which progress north was rapid, with Conwil station opening on 3 September 1860. At this time, the C & CR owned no rolling stock so they had to rely on the SWR to provide the service. This created tension between the two companies owing to excessive charges being levied and, as a result, the service was suspended on 31 December 1860. The company then hired two 4-4-0 tank engines and reopened the line with its own rolling stock on 15 August 1861. In October 1861 Bronwydd Arms, a new station between Carmarthen and Conwil, first appeared in company timetables.Progress north now slowed owing to problems during the construction of the 895yd Pencader tunnel (also known locally as Alltwalis Tunnel and Dolgran Tunnel). The digging required two construction shafts which could then be used for ventilation. Construction started in the spring of 1857, and digging initially proceeded from four sites - at either end and from the bottom of both ventilation shafts. Work was expected to be completed by December 1860/January 1861. The tunnel was 'finished' in March 1861 although, at that time, it was exposed rock without a brick lining and required further work to complete it. The long approach cuttings were also unfinished. During construction of the tunnel, many of the horses used to haul away excavated rock died from disease and were buried in the field surrounding the northern of the two shafts. The same field also has grassed-over rubble remaining from cottages built by the construction navvies. Much of the spoil excavated was used to build embankments north and south of the tunnel, but large spoil heaps can still be seen on the hillsides around both ventilation shafts.
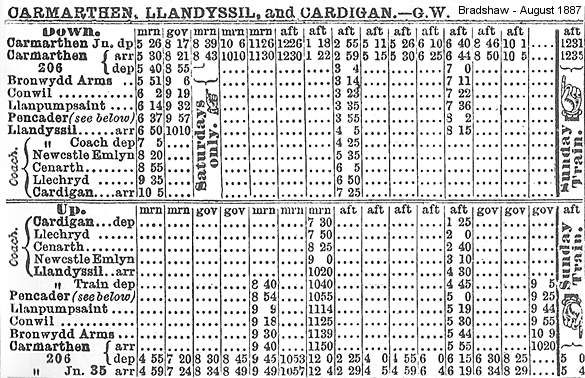
Further delays were caused by the original contractor, John Jay, abandoning the construction of the line in autumn 1861. By November, however, another contractor, Holdens, took over the construction. Work was then focused on finishing several miles of railway either side of the tunnel and, although easy to the north, to the south heavy engineering of cuttings and embankments slowed progress. The 12-mile extension to Cardigan was authorized by an Act of 1 July 1863 but it was never built. Track is known to have been laid through Pencader Tunnel at some point prior to December 1863. An official Board of Trade inspection was carried out in January 1864, and the tunnel opened with the rest of the Llanpumpsaint-Pencader section on 28 March 1864. At that time the tunnel was still unlined, and a watchman was employed to inspect it for any rock falls until it was eventually lined with brick some years later. The line reached Llandyssil, a further 3½ miles, on 3 June 1864 with a service of four trains in each direction, taking approximately 70 minutes between Carmarthen Town and Llandyssil. Most trains started or completed their journeys at Carmarthen Junction station. By now the high cost of construction, especially Pencader Tunnel and the purchase of two tank engines from Rothwell & Co, had drained the company’s resources and it was forced into bankruptcy. A Receiver was appointed to run the railway without any interruption to the service. In 1860 the Manchester & Milford Railway received Royal Assent to build a line from the C & CR at Pencader to Llanidloes. In 1861 a route was proposed north, mainly along the east side of the River Teifi valley from Pencader to Devil’s Bridge. There, a junction station would be constructed, with the main line proceeding to Llanidloes, and a branch line to Aberystwyth. By late 1864 the proposed route had changed, moving west from the original plan. This would result in both a shorter route to Llanidloes, and relocating the junction station from Devil’s Bridge to a new junction station near Ystrad Meurig. Parliamentary approval for the new route, to be built to standard gauge, was received in 1865 Work on the southern section of the line progressed rapidly, and the line from Pencader to Lampeter was opened on 1 January 1866. The M & MR made a junction with the C & CR half-a-mile north of Pencader. However, because of the gauge difference the two lines didn't actually join, and a new interchange station called Pencader Junction was opened with the new line. The next section from Lampeter to Strata Florida was completed by 1 September 1866, and the final section to Aberystwyth by August 1867. The South Wales Railway had been taken over by the GWR in 1862. By that time broad gauge was in decline and, in order to allow through running between the C & CR and the newly opened M & MR, the 13¾ miles from Abergwili Junction to Pencader Junction were altered to mixed gauge on 1 November 1866. The M & MR was given running rights into Carmarthen, but its trains were not permitted to call at intermediate stations. The C & CR directors regained control of their line in 1867. The remainder of the line to Llandyssil was converted to standard gauge on 1 June 1872, and all broad gauge running ceased from that date.
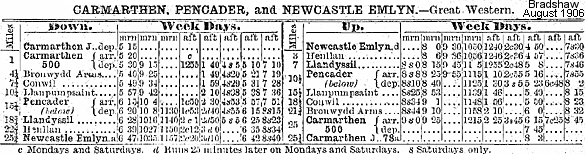
In September 1869 the C & CR formed a new company for extending the line to Newcastle Emlyn and eventually on to Cardigan, but the proposed extension failed to get sufficient local support. An approach was made to the London & North Western Railway to buy the line and build the extension to Newcastle Emlyn, but nothing came of this. In 1881, a Bill was put before Parliament authorising the C & CR to extend its line to Newcastle Emlyn, reduce the number of directors, and sell or lease its undertaking. On 4 March 1881 an Agreement leasing the C & CR to the GWR was approved by the House of Lords. Under GWR control the service was reduced to three down trains between Carmarthen and Llandyssil, but still four up trains The M & MR timetable of the same date showed three through trains in each direction between Carmarthen and Aberystwyth, with an extra morning service in each direction between Carmarthen and Lampeter. On 1 July 1882 the C & CR was absorbed into the GWR. All the necessary land for the extension was purchased by April 1885 but the GWR, who had been reluctant to build the line, ensured that work progressed as slowly as possible, taking over ten years to reach Newcastle Emlyn. The extension finally opened on 1 July 1895 with one intermediate station at Henllan. The long-awaited railway was given a riotous reception by the townspeople and traders of Newcastle Emlyn. The opening train was decorated with flags and flowers, and in the afternoon about two thousand people sat down to tea in the New Market House. In the evening a grand banquet was held in the Emlyn Arms Hotel.A further extension to Cardigan was now ruled out, largely because of opposition to the intrusion of the line into an area of natural beauty that had become a popular tourist attraction. Consequently the GWR had to make do with a motor bus service from Newcastle Emlyn to Cardigan. A second intermediate station called Pentrecourt Platform opened on 1 February 1912. The timetable for 1902 showed a daily service of four trains in each direction between Carmarthen and Newcastle Emlyn. On Saturdays there were two extra trains to Llandyssil only. There was no Sunday service. The M & M timetable for the same date shows four trains between Pencader and Aberystwyth, with three in the opposite direction. There was an early morning Saturdays-only train between Lampeter and Pencader, to connect with the morning Newcastle Emlyn to Carmarthen service. The Manchester & Milford Railway was leased by the Great Western in 1906 and absorbed in 1911. Carmarthen to Aberystwyth then became the main line, with the Pencader- Newcastle Emlyn line operated as a branch. The GWR opened a branch from Lampeter to Aberayron on 12 May 1911.
The Second World War brought a new lease of life as a relief route providing a vital link for northbound traffic, with regular movements of heavy munitions to Chester. After the war the line settled back to a quieter existence. With the ever-increasing popularity of the car, especially after WW2, the Teifi Valley lines clearly had no future under a nationalised British Railways. The Aberayron branch was the first to lose its passenger service from 2 February 1951. Passenger services lasted a little longer on the Pencader-Newcastle Emlyn branch, with the last train running on 13 September 1952. The main line enjoyed a brief resurgence in the 1950s when the Royal Train traversed the route, and other new traffic included Butlins through-specials taking holidaymakers to the new camp at Pwllheli. By the end of the fifties, there were three weekday trains each way (four on Saturdays) with a journey time of around 2½ hours with 16 timetabled stops and another 5 request stops. Declining passenger figures meant that the Beeching Axe was inevitable; in the end, however, it was nature that struck the first blow. Heavy flooding severed the line six miles from Aberystwyth in December 1964, in the same weekend that storms caused the Ruabon to Barmouth Line to suffer a similar washout. The last passenger train ran along the truncated route south of Strata Florida on 22 February 1965; inexplicably the BR network map dated 1965 showed Pencarreg, rather than Strata Florida, as the temporary northern terminus. The line remained open for freight using Hymek locomotives until around 1970, then by Class 37 locomotives. Despite closure to passengers, the branch lines also remained open for freight traffic. Withdrawal of freight facilities at individual stations started in December 1963. By 1965 freight-handling had ceased at all stations except Lampeter and Newcastle Emlyn, which then became railheads. Scheduled for complete closure at the end of 1972, the Newcastle Emlyn branch received a number of reprieves. The Teifi Valley Railway Preservation Society was formed in October 1972 with the intention of purchasing the Carmarthen-Newcastle Emlyn section for the operation of a steam-hauled tourist passenger service. Special excursion trains were chartered from British Rail giving hundreds of people their first opportunity of travelling on the line and seeing for themselves the outstanding countryside through which it passed.
Negotiations were opened with British Rail for the purchase of both land and track, and a stay of execution was obtained on the lifting of the line. However, the enthusiasts were faced with two insurmountable problems. Month by month the price of the track increased, frequently by tens of thousands of pounds, only to be aggravated by a serious shortage of steel, which put railway track at a premium. The second problem was the lack of local interest and support. Although offers of help poured in from all over the country, local working parties rarely attracted more than a dozen-or-so people, from a total membership of 200. The end came in 1973 for both the Newcastle Emlyn branch and the main line from Carmarthen to Lampeter with the end of the milk traffic. The last passenger train over both lines was the RCTS Farewell to the Teifi Valley Milk Branches railtour on 30 December 1972.
Two years after its closure, the Gwili Railway Preservation Company was formed with the ambition to preserve at least eight miles of track of the former route, from Abergwili Junction along the Gwili Valley to the station site at Llanpumpsaint. Track-lifting had already started by the time of the formation of the new company and, as a result, only a mile of track north of Bronwydd Arms was left in situ. The Company was, however, able to acquire the full eight-mile stretch of trackbed from Abergwili Junction to Llanpumpsaint for both rebuilding and preserving. Over time the railway has extended the operational length from one mile to 2½ miles, with its current northern terminus at Danycoed. The society is currently focusing its attention on a southward extension towards a proposed Carmarthen North station. Since the preservation society owns the trackbed as far as Abergwili Junction, two miles south of Bronwydd Arms, a new station can be constructed alongside the new Carmarthen eastern bypass. This will, hopefully, greatly improve visibility of the railway to passing traffic on this busy road compared to the less conspicuously sited Bronwydd Arms station. Once the southern extension of the Gwili Railway is complete, it will increase the length of the route to around 4½ miles. Reconnection with Carmarthen railway station is currently impossible as the bridge that once carried the line over the River Towy was demolished in the 1980s. Although attempts to preserve a standard-gauge line to Newcastle Emlyn were not successful, a restoration project eventually got under way in 1981 when a group of enthusiasts bought part of the trackbed at Henllan. In 1983, with the help of funding and labour from the Manpower Services Commission, they laid a 2ft-gauge track from Henllan to Pontprenshitw, where passengers were invited to take a short walk to admire the waterfall under the railway bridge. In 1987 the Teifi Valley Railway was extended as far as Llandyfriog and, since 2006, has been further extended to the current end of the line at Llandyfriog Riverside. During spring 2009 work proceeded to re-site Henllan station to its original location on the opposite side of the road. This new platform was brought into use in July 2009. Sources:
See other stations on the Carmarthen & Cardigan Railway: Carmarthen Junction, Carmarthen 1st, Carmarthen 2nd STILL OPEN, Bronwydd Arms, Conwil, Llanpumpsaint, Pencader, Pencader Junction, |
old1.jpg)
Copyright photo from John Alsop collection
old9.jpg)
Copyright photo by H C Casserley
old5.jpg)
old2.jpg)
old12.jpg)
Photo by John Mann
11.jpg)
Photo by Marion Phillips, reproduced from Geograph under creative commons licence
5.jpg)
Photo by Martin Potter
2.jpg)
Photo by Steve Chadney
1.jpg)
Photo by Brian Halford

|
| Last updated: Sunday, 21-May-2017 14:33:05 CEST |
© 1998-2012 Disused Stations
|



old8.jpg)
old7.jpg)
old11.jpg)
old_thumb9.jpg)
old_thumb10.jpg)
old_thumb6.jpg)
thumb4.jpg)
thumb6.jpg)
thumb12.jpg)
thumb7.jpg)
thumb3.jpg)
thumb8.jpg)
thumb9.jpg)
thumb10.jpg)
 Home Page
Home Page