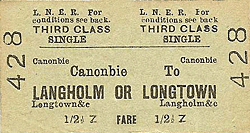
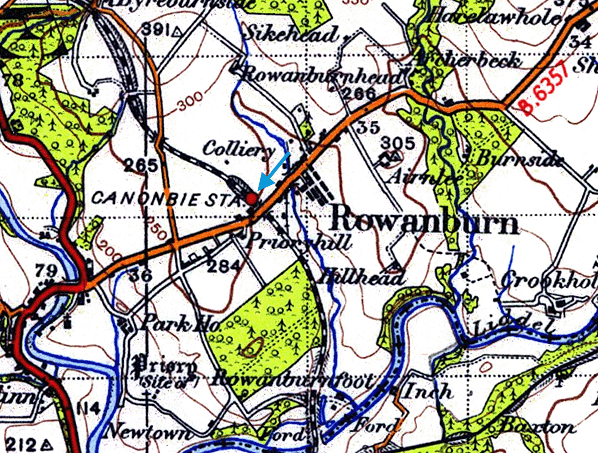
Notes: Delays in completing the Byreburn viaduct on the Langholm branch meant that the line was opened in stages, opening to Canobie in 1862. The station first appeared in public timetables in May that year. Although the village was generally known as Canonbie by this time the NBR adopted the original spelling until 1st February 1904 when the name was changed (see ticket below). A branch to the south of the station served Canonbie Colliery (also know as Rowanburn Colliery) from where there was a 485 yard narrow gauge line to the adjacent Binkbonny Colliery.
 |
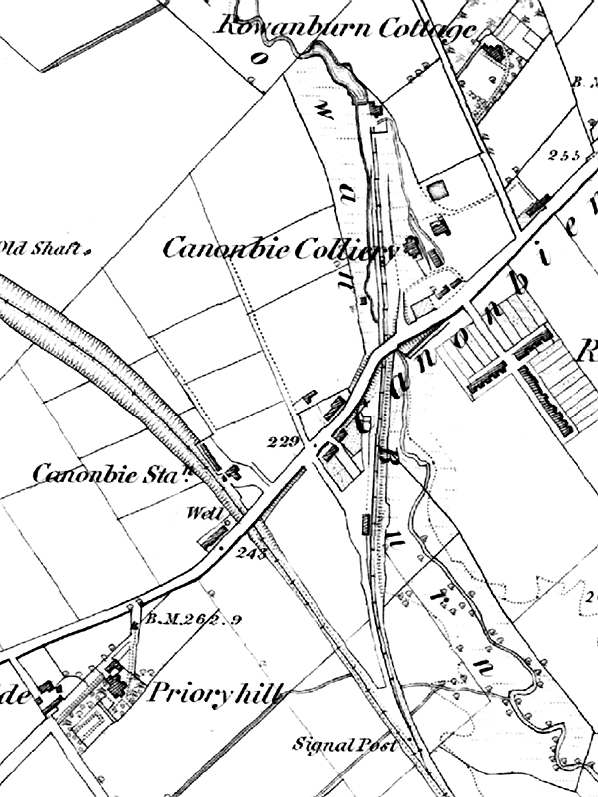
The colliery opened in the early eighteenth century. Initially much of the coal was used in the local limestone industry, but once the rail connection was established coal was sent to industry in the local area, as well as over the border into England. At the height of its production the mines employed over 100 men, and the Duke of Buccleuch built Rowanburn village (to |
the west of the station) for the workforce at that busy time. During 1915, and through the years of the Great War, coal was transported to the cordite manufacturing factory at Gretna known as H M Factory Gretna. Exhaustion of the workable coal seams brought large scale coal production to an end during 1922, and the colliery closed.
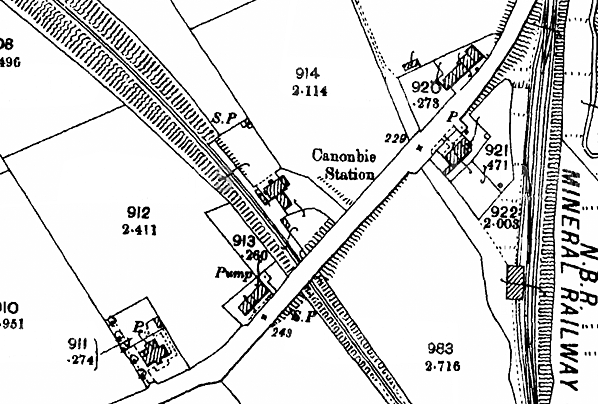
The station consisted of a single platform on the up side of the line and north of the level crossing. The single storey 'L' shaped stone-built stationmaster's house which incorporated the booking office was set back from the platform with a small stone waiting shelter and two timber 'sheds' (one an old goods wagon) on the platform.
The goods yard was on the south side of the road on the colliery branch. It comprised a loop serving a two-level cattle dock, with pens and a short spur at the north end of the loop to a timber goods shed. There was a 1 ton 10 cwt crane in the yard. The junction with the Langholm branch was controlled by the Canonbie signal box which opened in 1894. The box closed on 21st May 1921 and was replaced by a ground frame but with closure of the colliery in 1922 the siding taken out of use north of the Canonbie goods yard..
After closure to passengers in 1964 the station continued to handle goods traffic until 18th September 1967.
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE LANGHOLM BRANCH
The Border Union Railway, the Hawick branch of the North British Railway was opened on 1st November 1849. However, it was a further thirteen years before the Waverley Route was completed between Hawick and Carlisle. The last mail coach, from Hawick, ran on Monday, 30th June 1862, via Langholm to Canonbie, and the main line from Carlisle to Edinburgh was opened to regular traffic the following day.
In 1845, the North British Railway obtained powers to build the Hawick branch, and in the following session, they applied to Parliament for further powers to extend the line through Langholm to Carlisle. The Caledonian Railway opposed this extension, and in due course the North British Company’s plans were thrown out by the Government Committee. Matters dragged slowly on, with meetings in Hawick of many of the manufacturers who felt the need for a railway to the south. But no substantial progress was made until 1856 when a survey was made of the Liddesdale route. The Caledonian Railway also had plans for a station in the Lower Haugh in Hawick with a railway through Teviotdale and Langholm to Carlisle. (Over 1,500 women who used the Lower Haugh as a washing green objected to this scheme.)
| To the astonishment of many inhabitants, the claims of the Langholm line were approved and those of the Liddesdale scheme rejected. So indignant were the supporters of the Liddesdale railway, that a meeting outside the Town Hall in Hawick attracted some sixteen hundred people expressing the view that the decision was totally against the wishes of the people of |
 |
the south of Scotland. An appeal was taken to the House of Lords which resulted in the Langholm Bill being thrown out.
In 1859, the Railway battle raged again before Parliament and on Tuesday, 22nd March, it was announced that the Clydesdale scheme had triumphed.
Langholm had come close to having a through line to Hawick, worked by the Caledonian Railway Company, who would have built another station in Hawick away from the existing North British one.
 |
As a consolation to the people of Langholm, the train fare north of the town to Hawick and beyond was calculated as if the line ran direct and not south to Riddings before going north again. This led to the strange situation that the fare from Langholm to Edinburgh was cheaper than the fare from Canonbie to the capital, although Canonbie was some six railway miles nearer!
In many ways, Langholmites felt cheated. However, with the benefit of hindsight, perhaps a Caledonian Railway branch through Langholm to Hawick would not have served the town as well as inhabitants would have wished. Kelso had a station shared by the North British and the North Eastern railway companies, who although nominally friendly, did not always run trains to allow through connections from St. Boswells to Berwick. Both the Caledonian and North British |
Railway companies (who were arch rivals) had separate stations in Peebles but little effort was made to allow traffic to interconnect between the stations. Perhaps Langholm people would have experienced great difficulty in making a day trip to Edinburgh via Hawick. They might have found themselves, and the goods manufactured in the town, routed to the south to Carlisle by the Caledonian Railway and then north by that company’s main line via Beattock to Edinburgh – with all the revenue going to the Caledonian Railway. Via Hawick, of course, the revenue would have been shared with the North British Railway Company.
season.gif) |
Thus Langholm, its inhabitants, and its blossoming industries, had to be content with a seven-mile single-track branch line, although a mainline through the town, with direct connections to the north and south, worked by the same railway company from Edinburgh to Carlisle would have been the ideal situation.
The line opened to Canobie (note original spelling) in 1862 but it was a further two years before the Byreburn viaduct was completed with the first train arriving in Langholm on |
Tuesday, 29th March 1864, carrying the turntable to be installed in the yard. The extension was officially inspected the following Monday. The local paper records that passenger and goods traffic to Langholm started on Monday, 11th April 1864 although the official opening date is recorded as 18th April.
totty.gif) |
Less than a month had gone by before apprehension was expressed by a number of ‘self elected inspectors’ at the state of Byreburn viaduct (where one of the piers went as far below the surface of the burn as it was above). Subsidence caused by a slippage into the old coal workings had resulted in the collapse of a portion of the crown of the third arch from the Canonbie end of the viaduct. Trains were halted at each side of the viaduct, and passengers had to walk across the unsafe portion! In early May 1864 the Langholm to Canonbie train service was temporarily discontinued and the horse-drawn omnibus reinstated.
Feelings ran high in the town. It was felt that, having obtained the monopoly of train services, the North British Railway Company was being tardy in its efforts to resume the service. Mr H Dobie, the acting Chief Magistrate, stated that the line should have been kept open as it had been in the week following the slippage. He decided that a statement would be laid before the
|
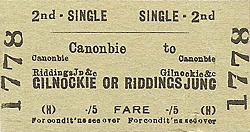 |
railway directors and if necessary, the whole matter would be brought before the Board of Trade. It is believed that a staging post north of the viaduct at Gilnockie was established at this time to serve an intended station. In due course the railway reopened on Monday 2nd November 1864, with six passenger trains running on weekdays and two on Sundays. A new station at Gilnockie opened in December 1864.
By 1906 there were 7 passenger trains in each direction but no Sunday service. By 1922 this had dropped back to 6 trains in each direction which was maintained until closure, but in the 1950s some trains ran through Gilnockie (which was unstaffed after 1953).
A letter in the Eskdale and Liddesdale Advertiser in December complained about the “unholy” Sabbath trains. The Sunday trains were discontinued in February 1865, the reason being given that they did not pay. The local paper commented, “The Sabbath rest will be a great boon to the employees along the branch, who, we understand, outnumber the passengers travelling from Langholm on the Sabbath-day.” No more Sunday trains ran in the next hundred years, except for the occasional excursion.
The branch line on crossing Liddel Viaduct at Riddings Junction entered England. But how many passengers knew that just south of Riddings the Waverley Route, through a quirk of ancient boundaries, crossed back into Scotland for 7 chains, then returned finally to England? A day visit to Carlisle from Langholm involved crossing the Anglo- Scottish Border six times ~ surely some sort of record?
Ironically, the very last passenger train, an enthusiasts’ special from Glasgow, ran on Sunday, 29th March 1967, almost three years after the line had been closed to regular passenger traffic. The Sabbath-breaking locomotive had difficulty running round its five-coach train, catching the last coach and removing splinters from its side.
The branch line and the successive railway companies, the North British, the London and North Eastern Railway and finally British Railways served the town well during times of both peace and strife. Everyday traffic included textiles, coal, newspapers, post, whisky (until the distillery closed), general merchandise and parcels. Single-coach steam railcars, usually 'Nettle' or 'Protector' were introduced on some services between the wars. Unusual traffic included specials to the new munitions factory at Gretna during WWI and, in WWII, double-headed trains drawing tanks to and from the Camp on the Castleholm. On occasions the Cornet’s horse came by rail.
However, after WWII, the use of private transport increased and, in common with rural branches all over Britain, the number of passengers using the Langholm branch decreased to the extent that the passenger service became uneconomic.
4.gif) |
When the Beeching plans were announced in 1962, the Langholm Branch and the Waverley Route were proposed for closure. A public meeting was held in the Buccleuch Hall in Langholm on 18th October 1963, when representatives of Langholm Town Council and other objectors were able to put forward their cases of hardship to members of the Transport Users’ |
Consultative Committee. Both oral and written objections were considered by the Committee, their unanimous conclusion being that, although it would be inconvenient to some, and might even cause hardship to a few, the closure of the branch would go ahead. The end was, however, inevitable, in 1964 only 350 passengers were using the 32 trains a week. The Beeching ‘Axe’, which meant that the sound of a train would never be heard again in many rural valleys, fell in Eskdale on 15th June 1964, with the last passenger trains leaving Langholm for Carlisle on Saturday 13th June. Many local people and train enthusiasts made a last-day trip over the seven-mile branch line.
The line remained open for freight traffic with three trains a week, although the layout at Langholm station was simplified with the removal of the track beside the platform. The very last passenger train was the Branch Line Society/Stephenson Locomotive ‘Society Scottish Rambler No. 6’ railtour from Glasgow on Sunday 26th March 1967. The Sabbath-breaking locomotive had difficulty running round its five-coach train, catching the last coach and removing splinters from its side. The freight service lasted until 17th September 1967.
Click here for a more detailed history of the Langholm branch.(8.3M pdf file). For additional photographs see the Langholm Archive Group web site. Some of their photographs are reproduced here with permission.
Click here to see a 4 minute film of the Langholm branch featuring all stations c.1964
Click here to see a 3.37 minute film of a freight workings (diesel and steam) on the Langholm branch
Brief history by Bruce McCartney, tickets from Michael Stewart (except 0405 and season ticket Bruce McCartney) route map drawn by Alan Young, timetable from Chris Totty
Sources:
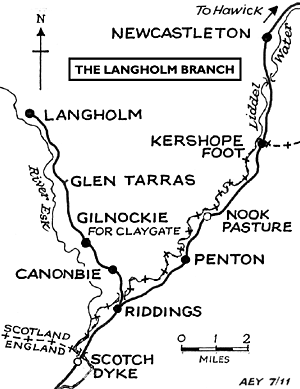
To see other stations on the Langholm branch click on the station name:
Langholm, Glen Tarras. Gilnockie & Riddings Junction
|

old6.jpg)
old4.jpg)
old1.jpg)
old17.jpg)
old11.jpg)
old3.jpg)
old9.jpg)
1.jpg)





season.gif)
totty.gif)
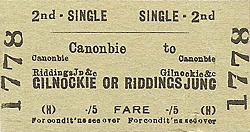
4.gif)

 Home Page
Home Page